Conducting a business lookup in Washington State is a crucial step for individuals, entrepreneurs, and organizations seeking to establish, expand, or verify the existence of a business entity within the state. The Washington State Secretary of State's office, specifically the Corporations and Charities Division, is responsible for maintaining records of all business entities registered in the state. These records include detailed information about corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), limited partnerships (LPs), and other business types. Utilizing the Washington State business lookup tool, accessible through the Secretary of State's website, allows users to search for business entities by name, Uniform Business Identifier (UBI) number, or other identifiers.
Why Perform a Washington State Business Lookup?

There are several compelling reasons to conduct a business lookup in Washington State. For potential investors, partners, or clients, verifying the legal existence and good standing of a business is essential. This due diligence helps mitigate risks by ensuring that the business is properly registered and compliant with state regulations. Furthermore, for entrepreneurs planning to start a new business, a lookup can help identify available business names, avoiding potential naming conflicts and trademark issues. Additionally, existing businesses may use the lookup tool to verify their own status or to research competitors and market trends.
How to Use the Washington State Business Lookup Tool
The process of performing a business lookup in Washington State is straightforward and can be completed online. First, navigate to the Secretary of State’s website and locate the business lookup tool. This tool allows users to search by business name, UBI number, or other specific identifiers. Once the search criteria are entered, the database returns relevant information, which may include the business entity type, registration date, status (active, inactive, or dissolved), principal office address, and names of registered agents or governors. It’s essential to verify the accuracy of the information, as it reflects the current status of the business with the state.
| Search Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Name | Full or partial name of the business entity |
| UBI Number | Unique identifier assigned by the state |
| Principal Name | Name of the individual or entity responsible for the business |

Understanding Business Entity Types in Washington State
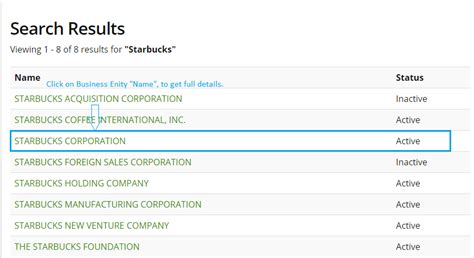
Washington State recognizes several types of business entities, each with its own advantages and requirements. The most common types include sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs). Each entity type has distinct characteristics, such as liability protection, taxation, and management structure, which are crucial considerations for business owners. For example, corporations offer strong liability protection but are subject to double taxation, whereas LLCs provide pass-through taxation and flexibility in management but may have higher annual reporting requirements.
Registering a Business in Washington State
Registering a business in Washington State involves several steps, starting with choosing a unique business name that complies with state naming requirements. Next, business owners must prepare and file the appropriate formation documents with the Secretary of State’s office, such as Articles of Incorporation for corporations or Articles of Organization for LLCs. Additionally, registering for necessary licenses and permits, obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, and opening a business bank account are essential steps in establishing a legally recognized business entity. It’s advisable to consult with a legal or business professional to ensure all requirements are met and to understand the ongoing compliance obligations.
Key Points
- Conducting a Washington State business lookup is essential for verifying the existence and status of a business entity.
- The lookup tool on the Secretary of State's website allows searches by business name, UBI number, or other identifiers.
- Understanding the different business entity types and their characteristics is crucial for making informed decisions about business structure.
- Registering a business in Washington State involves choosing a unique name, filing formation documents, and obtaining necessary licenses and permits.
- Ongoing compliance with state regulations, including annual reports and license renewals, is necessary to maintain good standing.
In conclusion, performing a Washington State business lookup is a vital part of doing business in the state, whether for due diligence, business planning, or compliance. By understanding how to use the lookup tool, the characteristics of different business entities, and the process of registering a business, individuals and organizations can navigate the complexities of business operations in Washington State with confidence.
What is the purpose of a UBI number in Washington State?
+The Uniform Business Identifier (UBI) number is a unique identifier assigned to each business entity by the state of Washington. It is used to track and identify businesses for filing and reporting purposes.
How do I register a new business in Washington State?
+To register a new business, you need to choose a business name, prepare and file the appropriate formation documents with the Secretary of State’s office, and obtain any necessary licenses and permits. It’s recommended to consult with a legal or business professional to ensure all requirements are met.
What is the difference between a corporation and an LLC in Washington State?
+A corporation offers strong liability protection but is subject to double taxation, meaning the business income is taxed at the corporate level, and then the dividends distributed to shareholders are taxed again at the personal level. An LLC, on the other hand, provides pass-through taxation, where the business income is only taxed at the individual level, and it offers flexibility in management structure. However, LLCs may have higher annual reporting requirements and fees compared to corporations.



