The Place of Service (POS) codes are a set of codes used to identify the location where a medical service was provided. These codes are an essential part of the medical billing process, as they help determine the reimbursement amount for healthcare services. The POS codes are used by healthcare providers to indicate the setting in which a service was rendered, such as a physician's office, hospital, or outpatient facility.
The POS codes are maintained by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and are updated periodically to reflect changes in healthcare delivery settings. The codes are used in conjunction with other billing codes, such as the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, to provide a complete picture of the medical service provided. Accurate use of POS codes is crucial, as incorrect coding can result in denied claims or reduced reimbursement.
Key Points
- The Place of Service (POS) codes identify the location where a medical service was provided.
- POS codes are used in conjunction with CPT codes to determine reimbursement amounts.
- Accurate use of POS codes is essential to avoid denied claims or reduced reimbursement.
- The CMS maintains and updates the POS codes to reflect changes in healthcare delivery settings.
- Healthcare providers must use the correct POS code to indicate the setting in which a service was rendered.
Place of Service Code Categories
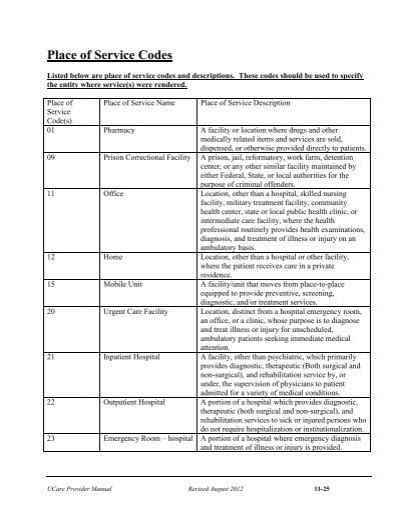
The POS codes are categorized into several groups, each representing a different type of healthcare setting. The categories include:
- Office settings (e.g., physician's office, clinic)
- Hospital settings (e.g., inpatient, outpatient, emergency department)
- Outpatient facilities (e.g., ambulatory surgical center, dialysis center)
- Home care settings (e.g., home health agency, hospice care)
- Other settings (e.g., skilled nursing facility, rehabilitation center)
Each category has its own set of POS codes, which are used to indicate the specific location where a service was provided. For example, the POS code for a physician's office is 11, while the POS code for a hospital outpatient department is 22.
POS Code Examples
The following are examples of POS codes and their corresponding descriptions:
| POS Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 11 | Office |
| 22 | On campus outpatient hospital |
| 23 | Emergency room - hospital |
| 24 | Ambulatory surgical center |
| 31 | Skilled nursing facility |
These codes are used to provide a detailed description of the healthcare setting in which a service was provided, allowing payers to accurately determine reimbursement amounts.
Importance of Accurate POS Coding
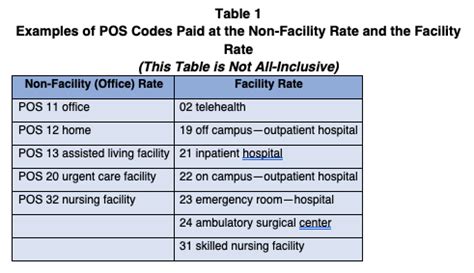
Accurate POS coding is essential to avoid denied claims or reduced reimbursement. Incorrect POS coding can result in:
- Denied claims: If the POS code is incorrect, the claim may be denied, and the healthcare provider may not receive reimbursement.
- Reduced reimbursement: If the POS code is incorrect, the reimbursement amount may be reduced, resulting in lost revenue for the healthcare provider.
- Audit risks: Inaccurate POS coding can increase the risk of audits, which can result in fines and penalties for healthcare providers.
Healthcare providers should ensure that they use the correct POS code to avoid these consequences and ensure proper reimbursement for their services.
Best Practices for POS Coding
To ensure accurate POS coding, healthcare providers should follow these best practices:
- Verify the POS code with the payer: Healthcare providers should verify the POS code with the payer to ensure that it is accurate and up-to-date.
- Use the correct POS code for each service: Healthcare providers should use the correct POS code for each service provided, rather than using a default code.
- Keep records of POS code usage: Healthcare providers should keep records of POS code usage to ensure that they can track and audit their coding practices.
By following these best practices, healthcare providers can ensure accurate POS coding and avoid denied claims or reduced reimbursement.
What is the purpose of Place of Service (POS) codes?
+The purpose of POS codes is to identify the location where a medical service was provided, allowing payers to accurately determine reimbursement amounts.
How often are POS codes updated?
+POS codes are updated periodically by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to reflect changes in healthcare delivery settings.
What are the consequences of incorrect POS coding?
+Incorrect POS coding can result in denied claims, reduced reimbursement, and increased audit risks.
Meta Description: Learn about Place of Service (POS) codes, their importance in medical billing, and how to ensure accurate coding to avoid denied claims or reduced reimbursement.



